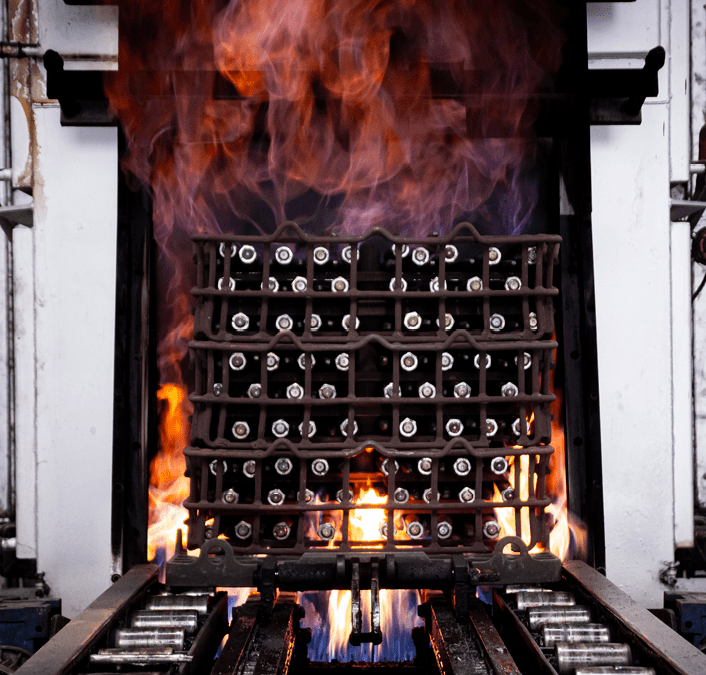
OUR HEATTREATMENTS
HEAT TREATMENTS
OF METALS
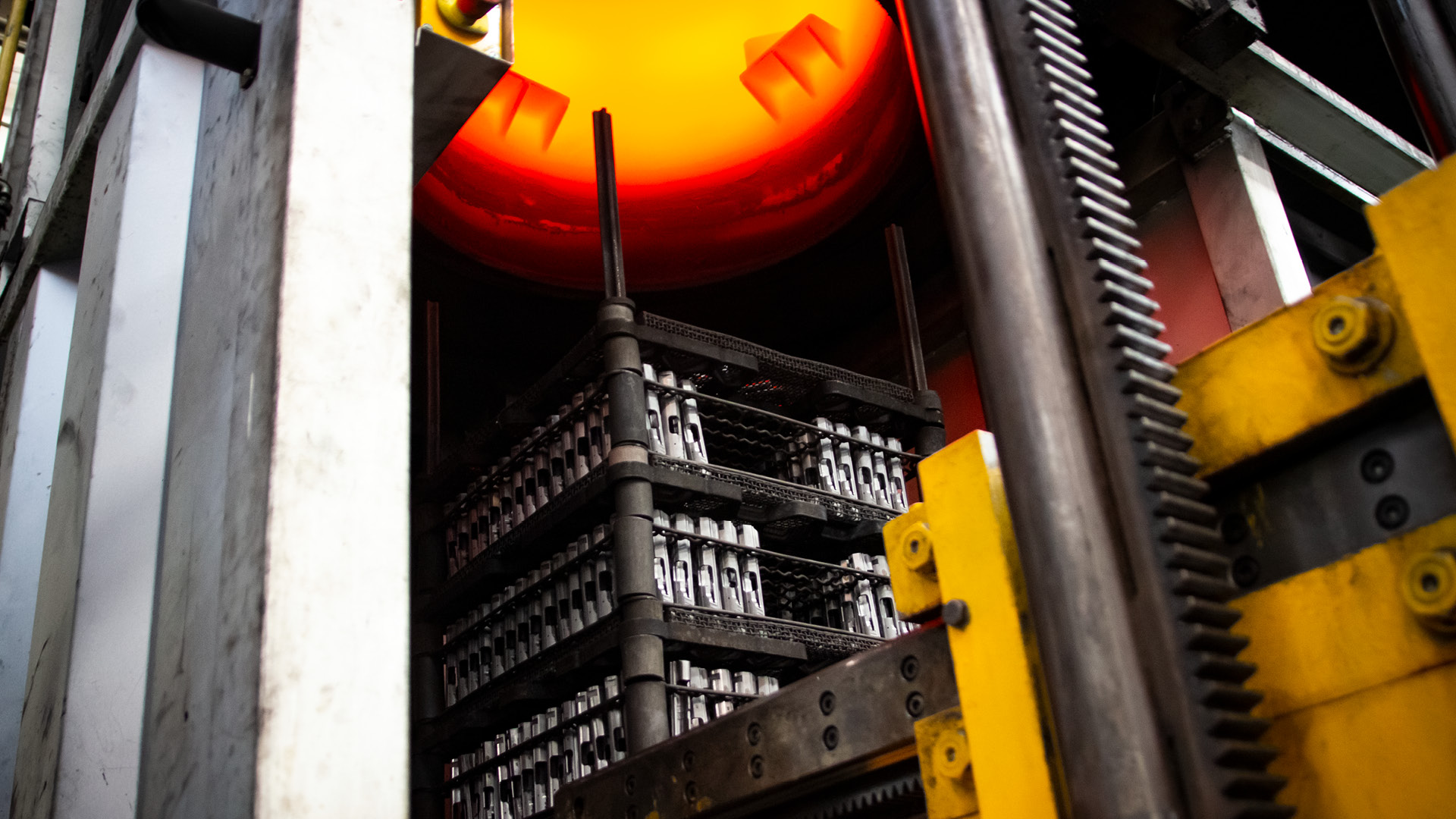
Heat treatment can be defined as the thermal heating cycle (at different temperatures) followed by more or less slow cooling, to give a metal those crystalline structures that give it certain mechanical and/or technological characteristics.
The effect of heat treatments on the structure of a metal alloy is an important field in materials science and its understanding is crucial to obtain from a material the desired characteristics with the greatest accuracy.
STEEL
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Quenching and tempering
-Normalizing
-Annealing
-Stress Relief/ Stabilization-Subzero treatment
-Carburizing
-Recarburization
-Carbonitriding
CARPENTERY
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Stress relief;
-Normalizing;
-Annealing;
-Ferritization annealing;
-Customed cycles.
NON-FERROUS ALLOYS
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Solubilization and artificial aging (T6):
-Solubilization and natural aging (T4);
-Solubilization and partial Aging (T64);
-Artificial aging on aluminium (T5);
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Stress relief;
-Sampling on small batches;
-Solubilizations;
-Annealing;
-Customized cycles (on customer’s specific instruction)
HEAT TREATMENTS
Heat treatment can be defined as the thermal cycle of heating at different temperatures carried out in predetermined conditions (controlled atmosphere or not) which must be followed by more or less slow and / or isothermal cooling, to give a metal or a metal alloy (alloys ferrous or non-ferrous) those crystalline structures that give it certain mechanical and / or technological characteristics.

The effect of heat treatments on the structure of a metal alloy is an important field in materials science and its compression is crucial to obtaining the desired characteristics with greater accuracy.
The binary or ternary state diagrams of an alloy are not sufficient to predict which phases will be obtained after the treatment cycle since they foresee the phases in equilibrium conditions as a result of long periods at certain temperatures. What happens in the practice of heat treatments is that at certain cooling rates different metastable structures are obtained which give the material the required characteristics.
The addition of a controlled atmosphere in the furnace chamber changes the chemical composition of the surface layer of the alloy, this process is defined as a thermochemical treatment.
STEEL
HEAT TREATMENTS
– Quenching and tempering
– Normalizing
– Annealing
– Stress Relief/ Stabilization
– Subzero treatment
– Carburizing
– Recarburization
– Carbonitriding
CARPENTRY AND CAST IRON
HEAT TREATMENT
– Stress relief;
– Normalizing;
– Annealing;
– Ferritization annealing;
– Customed cycles.
NON-FERROUS ALLOYS
HEAT TREATMENTS
– Stress relief;
– Normalizing;
– Annealing;
– Ferritization annealing;
– Customed cycles.
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Stress relief;
-Sampling on small batches;
-Solubilizations;
-Annealing;
-Customized cycles (on customer’s specific instruction)
STEEL
HEAT TREATMENTS
– Quenching and tempering
– Normalizing
– Annealing
– Stress Relief/ Stabilization
– Subzero treatment
– Carburizing
– Recarburization
– Carbonitriding
CARPENTRY AND CAST IRON
HEAT TREATMENT
– Stress relief;
– Normalizing;
– Annealing;
– Ferritization annealing;
– Customed cycles.
NON-FERROUS ALLOYS
HEAT TREATMENTS
– Stress relief;
– Normalizing;
– Annealing;
– Ferritization annealing;
– Customed cycles.
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
HEAT TREATMENTS
-Stress relief;
-Sampling on small batches;
-Solubilizations;
-Annealing;
-Customized cycles (on customer’s specific instruction)